
English vocabulary and phrases on Mid-Autumn Festival
Join EnglishVocabulary to immediately learn important knowledge about PAST PERFECT tense with formulas, signs, and exercises with detailed answers. Besides, you should practice the past perfect tense to consolidate your knowledge for all tests.
The past perfect tense is used to describe an action that occurred before another action, both of which took place in the past. The action that happened first uses the past perfect tense, while the action that happened later uses the simple past tense.

Examples of the Past Perfect Tense
S + had + past participle
Examples:

S + hadn’t + past participle
Where hadn’t = had not
Examples:
Question word + had + S + past participle
➣ How to answer:
Yes, S + had.
No, S + hadn’t.
Examples:
To know when to use the past perfect tense, you need to understand the specific cases and situations to avoid confusion with the simple past tense.
Examples:
Examples:
Examples:
Examples:
Examples:
This usage is often seen in past wish structures.
Examples:
The past perfect tense is often recognized by certain conjunctions.

Examples:
4.2.1. When
Example:
4.2.2. Before
Before “before,” use the past perfect tense; after “before,” use the simple past tense.
Example:
4.2.3. After
Before “after,” use the simple past tense; after “after,” use the past perfect tense.
Example:
4.2.4. By the time
Example:
4.2.5. No sooner… than…
This is an inversion structure used only with the past perfect tense. Formula:
No sooner + had + Subject 1 + Verb 1 (V3/V-ed) + than + Subject 2 + Verb 2 (V2/V-ed)
Subject 1 had just done something when Subject 2 did something else immediately.
Examples:
4.2.6. Hardly/Barely/Scarcely … when …
This is an inversion structure used only with the past perfect tense, synonymous with “No sooner… than…” Formula:
Barely/Hardly/Scarcely + had + Subject 1 + Verb 1 (V3/V-ed) + when + Subject 2 + Verb 2 (V2/V-ed)
Subject 1 had just done something when Subject 2 did something else immediately.
Note: Subject 1 and Subject 2 can be the same or different.
Example:
Differentiating between the past perfect tense and the past perfect continuous tense in English can be challenging for many learners. Below is a comparison of the two tenses.
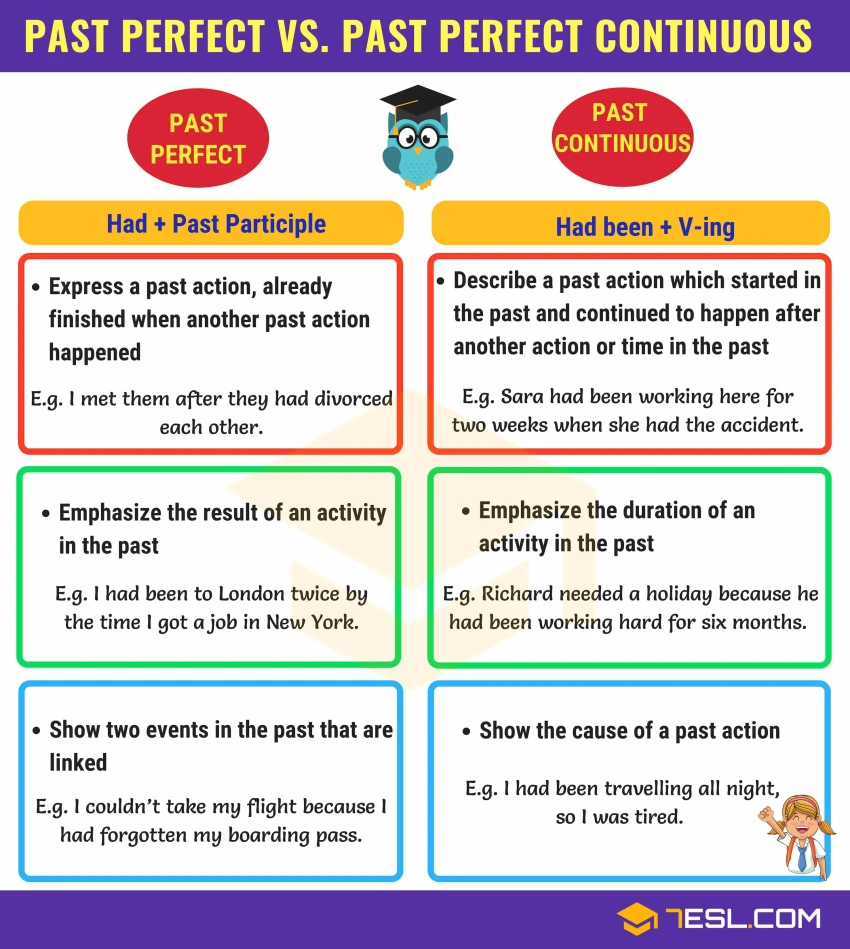
Past perfect tense exercises 1
Past perfect tense exercises 2
Past Perfect Exercise 3

English vocabulary and phrases on Mid-Autumn Festival

Tips to improve vocabulary in communication

English vocabulary by topic: Clothes

The secret to remembering all 50 English vocabulary words every day easily

English vocabulary by topic: Human body

Vocabulary of the most popular subjects in English

Learn English about Covid: All about vocabulary and disease prevention

Vocabulary of Subjects in English

Set of 60 English vocabulary on educational topics

Vocabulary - just a small thing!
Comment ()